For as much as we glorify the medical profession it is actually a much simpler job than it seems. Don’t get me wrong, being a medical provider requires years of training and experience. In the developed world, medical providers are held to extraordinarily high standards. They should be as they are compensated very well for their responsibilities and we need their skills. My observation has less to do with expertise and more about attitude.
“How can I help you?”
This simple question should summarize our relationship with our patients by placing us in a role of service to our patients. Unfortunately, all too often, the question is presented more in the light of “What is the problem?”. This slight difference in language changes our role and places patients in our service rather than us being in theirs.

Nothing could be more clear in the developing world than the disparity between those who have money and those who don’t. People with money receive good access to medical care and are generally regarded with respect when visiting a clinic or hospital. Those who don’t have money, well… they are ignored. In Nepal, I have witnessed on many occasions, doctors who never made eye contact with their patients. I have seen them talk on their cell phone while they rifle though the patient’s records and summarily write prescriptions, sending their patient on their way without so much as two words exchanged. For the patient, this impersonal visit is often at the cost of their family’s land and livelihood. Again, there are many doctors who do very fine work and I’m not denying that hospitals, doctors, labs and technology do not cost real money —of course they do. As professionals, we need to make a living the same as everyone. The question is more one of, how do we serve our patients equally? How do we see each human being as a unique and valuable part of our community, equally entitled to our attention? For that, our profit driven system seems to fail us.

This year, I worked with one of our volunteer practitioners trying to manage a very persistent outer ear infection in a young Tamang girl. After several weeks of treatment with saline and vinegar flushes, topical herbs, oral and topical antibiotics, and topical anti-fungal agents, she still presented with a deep abscess just above the tympanic membrane. We referred her for a tuberculosis test to rule out a rare form of skin TB. It came back negative. Here is where it gets difficult for us, because we run up against the family’s ability to pay for other more extraordinary care. We appealed to the District Health Office for assistance and they requested that we obtain a referral from the local health post. After consulting with the doctor at the heath post, she agreed that the girl needed surgery to clean and close the abscess. However, she declined to write us the referral because “She [the patient] can’t afford the surgery, so what is the point.”
Now, dear reader, please don’t worry. These road blocks do not stop us and we generally find a way to help our patients. It is also not my intention to single out this one doctor because this is an attitude that pervades the entire health system. I would like to say it pervades the system “in Nepal” but I feel the problem is more far-reaching.
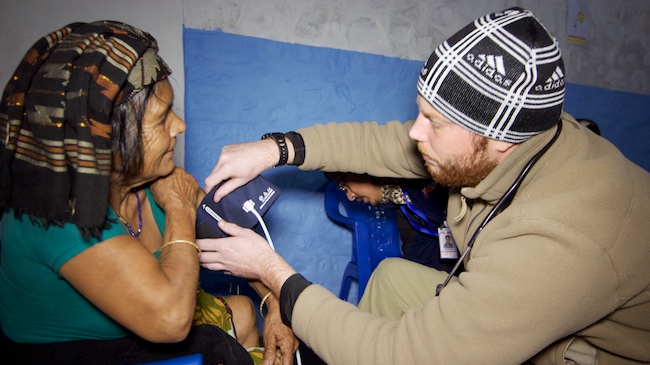
In my mind I ask, how can this be an acceptable response? How can it make sense to allow a persistent infection progress into permanent hearing loss or worse? How can that possibly serve the community?
In Nepal, the answer is that the doctor is not a part of the same community. He or she is separated by a gulf of education, opportunity and other socio-economic advantages. Doctors lose sight of the purpose of their service.
The other issue is that healthcare providers often don’t look beyond their own conclusions for treatment. When we have been trained to think an abscess equals surgery, it is hard to back away from that edge in order to think about other possible solutions or approaches. To remedy this, we need to take a more holistic approach to patient care. On an individual level, we talk about holism in the context of the patient, where we don’t just look at the disease process but rather we look at the whole person and how the disease is effecting their overall wellbeing. We need to extend this thinking to how we look at our overall system of delivering care. Instead of looking at medicine as individual modalities or treatment specialties, we need to go back to pondering how we can best alleviate a patient’s suffering. Often times it has more to do with providing information and education than it has to do with intervention, but it is impossible to arrive at this conclusion if we immediately jump to treatment.
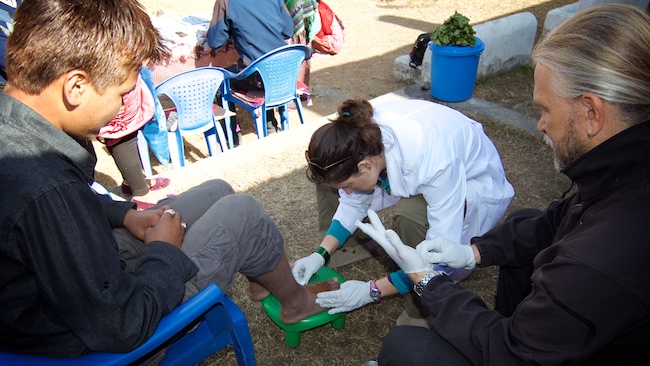
Look at the fact that many research studies [1][2][3] show that the strength of the patient/practitioner relationship has a direct correlation to the patient’s medical outcome and it should be obvious that treating each and every individual with kindness and respect should go without saying. Yet, in my experience, this relationship seems to be lacking. This is especially true in the rural areas of Nepal where our patients are mostly illiterate and lack the education to ask even the most basic questions about their health. The doctor (I use this term loosely because usually the patient is seeing a health assistant and not a doctor) asks “what is wrong with you?” and then prescribes them a list of medications. Of course the patient has no idea what the medications do, they just believe that they will be cured. When they are not cured, they do not know what to do next. We have found that by just taking the time to clean an infected wound while explaining how to use simple soap, water and exposure to direct sunlight not only kills the infection and heals the wound but also prevents future infections. This simple practice injects new information into the community and effectively inoculates many would-be patients through dissemination. This is so much less-expensive and safer than the common practice of treating superficial infections with antibiotics.

At our clinics, we have the advantage of seeing our patients many times and we start to know them and their families. We laugh and joke with our patients (something unheard of in Nepal) and we start to understand their unique needs. We earn their trust and that trust allows us to help them in ways that transcend medical intervention. I am certain that our volunteers get tired of me telling them that a patient has the right to know their diagnosis. They should know the details of the prescribed plan (or medications) and what the expected outcome is. It is so simple. However, throughout Nepal’s medical system (and probably our own), patients lack this basic information. If they were armed with this information, they could make their own choices regarding their care. They could agree to be served by us, they could seek other advice, or they could do nothing. It would be in their hands.

This year we hosted our first ever formal community and press meeting. We invited our patients, community leaders, district health officials and members of the local and national press to hear what we have accomplished in Nepal and our ideas on transforming the rural care system. It was sort of a grandiose plan but it was very well attended and received. The District Health Chief spoke very highly of our service in Makawanpur and pledged his support in looking at a more holistic model of providing care. He introduced us to a new area in Makawanpur called Bajra Barahi which is regarded as a model health post in Nepal. Their development committee listened to our presentation with interest but also a heathy amount of skepticism. They had experienced several disappointments from other NGO’s who promised large benefits but delivered shoddy medicine with many poor outcomes. They were also very concerned about the sustainability of our efforts.

My response was simple. “We either earn the trust of your community and show you that we can be effective or else it doesn't matter if we are sustainable or not. We offer a simple, safe and effective addition to your health system in which we work side-by-side in partnership with your existing staff and facilities. If we show you that our system is effective, it is easy to adopt and sustain without us. We will show you how and you will have a model which you can share with every district of Nepal.”

They were satisfied with that answer and in the weeks that followed many doors opened for us. Baja Barahi’s development committee offered to give us a small clinic building and land within the existing health post compound. This new partnership with the district government has been the opportunity I have been looking for since beginning this project in 2008. It is our first opportunity to not only care for patients, but to start working on transforming the rural care system as a whole. In other words, now we have the opportunity to put-up or shut-up.


This is quite the mandate and to meet this challenge we truly have to address our sustainability. Since beginning in Nepal, we have recognized that it is not practical or cost-effective to sustain our project with foreign practitioners. Unfortunately the problem of training and properly certifying acupuncturists has been a major obstacle. A system of accreditation and licensure does not exist and we envision training a type of health-care worker that does not yet exist. Ideally this hybrid “Rural Care” provider would be trained in both basic allopathic medicine (same as the existing health assistant) as well as acupuncture, bodywork and medicinal herbs. They would support other doctors, heath assistants and health post staff but also provide holistic health advice, simple and effective treatment and be an advocate for integrated patient care. In order to be useful in strengthening Nepal’s rural health system, these new providers would need to be able to work independently in some very remote regions.

Our solution materialized in the form of a small acupuncture school in Kathmandu that was struggling to get started. Founded by a Japanese NGO and staffed by a few Nepali acupuncturists that were trained in China, the Rural Health and Education Service Center (RHESC) was able to acquire certification through Nepal’s vocational education system in 2013. That is a start but falls short of certifying the kind of provider we are looking for. This year we were able to form an alliance with the RHESC and I was honored to be given a position on their Board of Directors. My task is to write a curriculum that will be accepted by Nepal’s Health Professions Council, allowing them to offer a bachelors degree in Acupuncture and Rural Health Care.

I had the privilege of teaching a five-day seminar on the shoulder joint to the RHESC’s second year students and was impressed by their appetite for opportunity and education. Our challenge is to inspire them to work in rural areas where they are needed most. Starting in September 2015, we will be hosting 12 RHESC students as clinical interns. This mentorship program will allow students real-world field experience under our guidance and offer the district government the opportunity to see the potential of future employment of RHESC graduates. We have encouraged several of our current interpreters to compete for government scholarships available to students in rural areas for enrollment in the RHESC program. This will be the key to sustaining our clinics in areas like Kogate which is too small for us to sustain a permanent clinic.


These are all just the first few wobbly steps in the right direction and while all of these developments are exciting prospects, I try to root myself in my own experience. From there I see that when it comes to patient care, sometimes I can have a major impact on a person’s life. Other times I struggle to offer even the slightest relief no matter how hard I try. Either way I hope that I never fail at making my patients feel cared for. With this simple idea, I believe we can make a ripple in a much bigger pond.
Author: Andrew Schlabach, MAcOM EAMP
Director, Acupuncture Relief Project
Bhimphedi, Makawanpur, Nepal











